May
22
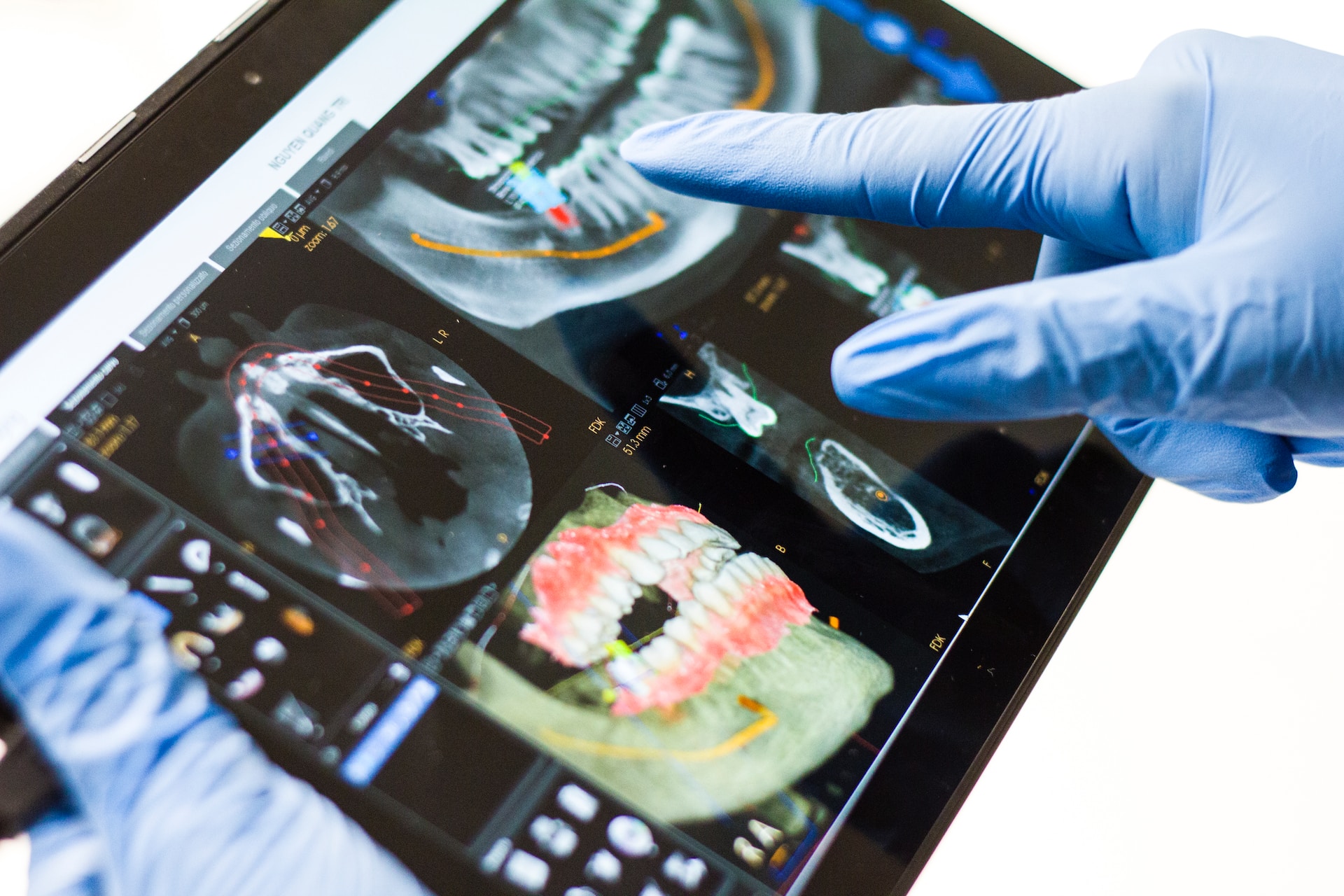
Oral health is a critical aspect of our overall well-being, often acting as a window to our overall systemic health. While most of us focus our attention on preventing tooth decay, the importance of gum health is frequently overlooked.
Receding gums are a common dental problem, and can have significant consequences, – including tooth loss – if left unaddressed. In the following comprehensive guide, we’re going to take a look at what receding gums are, their causes, symptoms, the link between receding gums and tooth loss, and finally, how to prevent this common oral health issue. Let’s take a look!
What are receding gums?
Receding gums, also known as gingival recession, refers to a condition in which the gum tissue that surrounds the teeth starts to pull back or wear away, thereby exposing more of the tooth or the tooth’s root. This situation can lead to “pockets” or gaps forming between the teeth and gum line, making it easy for disease-causing bacteria to build up. It’s a relatively common dental problem, often developing gradually, and can go unnoticed until significant gum recession or tooth sensitivity occurs.
What causes receding gums?
The cause of receding gums can be multifactorial, and often includes both genetic and environmental factors. One of the primary causes is periodontal disease, which is a bacterial gum infection that destroys gum tissue and supporting bone that hold your teeth in place. This is the main cause of gum recession in adults.
Other causes of receding gums include aggressive tooth brushing, which can wear down the enamel and cause the gums to recede. In addition to this, insufficient dental care – such as inadequate brushing and flossing – can also lead to tartar build-up, pushing the gum margin away from the tooth. Other contributing factors include hormonal changes in women, tobacco use, teeth grinding or clenching, and genetic susceptibility to periodontal disease.
Symptoms of receding gums
While the following symptoms can point to other dental and oral conditions, common symptoms of receding gums include:
- Red, swollen or tender gums
- Gums that bleed during and after brushing
- Persistent bad breath
- Loose teeth
- Visible tooth roots
- Long-looking teeth
- Discomfort or sensitivity to hot and cold
Do note that this is just general advice, and you’d need to consult with a dentist to know whether or not you do suffer from receding gums, and to be able to identify the source of the problem. As mentioned above, these symptoms can also be present with other gum and oral conditions.
Also Read: Can Receding Gums Be a Sign of an Underlying Health Condition?
Can receding gums lead to tooth loss?
So, can receding gums actually cause you to lose teeth? Unfortunately, receding gums can potentially lead to tooth loss. This is because the gum tissues serve as a protective barrier for the structures that hold teeth in place, including the underlying jawbone; when the gums recede, the roots of the teeth are exposed, and this can lead to tooth sensitivity, root damage, and eventual tooth loss. The ‘pockets’ or gaps that form between the teeth and gum line due to recession can also harbour harmful bacteria, leading to severe infections that can destroy the supporting bone structure.
How to prevent receding gums
So, how can you keep your gums as healthy as possible, and prevent both gum disease and its consequences? Here’s what we recommend:
Regular dental check-ups
Regular dental check-ups and professional cleanings are essential for your oral health, and you should aim to visit your dentist around once every six months. A professional dentist will be able to detect early signs of gum recession and prevent further damage by eliminating plaque and tartar build-up with a professional clean and polish.
Proper brushing and flossing technique
Your gums are inherently delicate, so using a soft toothbrush and avoiding aggressive brushing can help prevent gum damage. Try to use a soft-bristled toothbrush and never brush to the point of discomfort – lightly brush your gums applying mild pressure. Make sure to brush and floss twice daily.
Lifestyle changes
Like any other area of our body, lifestyle factors play a significant role in gum health. Practising good habits – such as avoiding tobacco and alcohol – can support gum health.
Orthodontic support
If you grind your teeth at night, a condition known as bruxism, using a custom-fitted mouthguard can help protect your teeth and gums from unnecessary strain and wear. This mouthpiece, usually recommended by your dentist, offers a barrier between your upper and lower teeth, thereby reducing the likelihood of gum recession.
A healthy diet
Diet also plays a key role in the health of your gums – just like any other area of your body. Consuming a balanced diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and fibre can strengthen your gums and teeth, thereby preventing gum recession. Specifically, vitamin C has potent anti-inflammatory properties that can prevent gum diseases. You’ll also want to think about limiting the intake of sugary foods and drinks, which provide a breeding ground for harmful bacteria in your mouth, is equally important. If you are going to be drinking sugary beverages, try doing so with a straw to prevent contact with your teeth and gums.
Read Next: 5 Foods for Healthy Gums










